
What Is WiFi 6?
WiFi 6 is the latest and most advanced WiFi technology. It offers faster speeds and better reliability than any previous version, making it ideal for busy households or offices with multiple devices connected at once.
-
Quick Links
What Does WiFi 6 Mean? What Is 802.11ax? What Is a WiFi 6 Router? How Fast Is WiFi 6? What are the Benefits of WiFi 6? WiFi 5 Vs. WiFi 6: What Is the Difference? WiFi 6 Vs. WiFi 6E What Device Support WiFi 6?
What Does WiFi 6 Mean?
The WiFi Alliance classifies WiFi 6 and its 6Ghz update WiFi 6E as the sixth generation of wireless local area networking standards compatible with the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.15.4. 1ax standards.
WiFi 6 enables devices to perform more efficiently in dense conditions. As a result, it offers several improvements over its predecessors. It delivers faster speeds, better reliability, and increased capacity to handle more devices simultaneously. This makes it ideal for busy households or offices with multiple devices connected at once.
The number 6 in WiFi 6 refers to the sixth generation of WiFi technology. The basic idea is that WiFi 6 routers can send and receive data more efficiently, allowing more devices to connect simultaneously without slowing down the network. This improved efficiency also reduces power consumption, so your devices will last longer on a single charge.
WiFi 6 is also backward compatible, meaning it will work with any device that supports earlier versions of WiFi. So if you're looking to upgrade your home or office network, consider a router that supports WiFi 6.
What Is 802.11ax?
802.11ax is the most recent version of the WiFi standard, offering faster speeds and better reliability than any previous version. It is also backward compatible, meaning it will work with any device that supports earlier versions of WiFi. 802.11ax is often referred to as WiFi 6 since it is the sixth generation of WiFi technology.

What Is a WiFi 6 Router?
A WiFi 6 router is a type of router that uses the WiFi 6 standard to connect devices to the Internet. The WiFi 6 standard is the latest and fastest way to connect to the Internet, and it offers many benefits over older standards like WiFi 5.
For example, WiFi 6 routers have improved range and can support more devices simultaneously. They also offer better security and are more energy-efficient. If you're looking for the best possible Internet experience, a WiFi 6 router is the way to go.
However, it's important to note that not all devices support WiFi 6’s enhancements. So if you're planning on upgrading your router, check that your devices can take advantage of the new standard.
How does WiFi 6 Work?
WiFi technology has come a long way since it was first introduced in the late 1990s. While WiFi 6 is the latest iteration of the technology, it works much like its predecessors.
Here's a quick overview of how WiFi works:
Your device, whether it's a laptop, smartphone, or tablet, connects to a router via radio waves. The router then sends and receives data from the Internet through a wired connection.
The router uses different channels to send and receive data. The number of channels available depends on the WiFi standard being used. For example, WiFi 802.11n (WiFi 4) supports up to four channels, while WiFi 802.11ac (WiFi 5) supports up to eight.
Of importance to note is that WiFi 6 works similarly to other versions. However, it adds the functionality and effectiveness to meet increasing connectivity demands in homes and offices.

How Fast Is WiFi 6?
While WiFi 5 offers 3.5 Gbps, you can expect as much as 9.6 Gbps from WiFi 6. This demonstrates the increased speeds WiFi 6 has to offer. However, these speeds are theoretical maximums, meaning you will likely not experience them.
In real-world scenarios, you can expect speeds around 600 Mbps with WiFi 802.11n (WiFi 4). But with WiFi 802.11ac (WiFi 5), you'll see average speeds of around 1200 Mbps. And with the new WiFi 802.11ax (WiFi 6) standard, you can expect to see average speeds of around 3000 Mbps.
Keep in mind that these are just averages, and your actual speed will depend on several factors, such as the number of devices connected to the network and the distance from the router. Your upload and download speeds will also never exceed the speeds that your Internet service provider (ISP) delivers to your home.
However, the fact that WiFi 6 boasts a far higher theoretical speed ceiling than its predecessor is still significant. The 9.6 Gbps signal can reach multiple PCs, provided they are all on the same network. Because it can be shared across the network of devices, each one becomes more likely to achieve its maximum speed potential than before.
What are the Benefits of WiFi 6?
When it comes to Internet connectivity, speed is essential. However, focusing on speed alone diminishes the true value of WiFi 6 as it offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Improved Security
One of the most significant benefits of WiFi 802.11ax is its enhanced security features. The new standard uses WPA-Enterprise and 256-bit encryption to protect your data from being intercepted by hackers.
-
Better Battery Life
Another advantage of WiFi 802.11ax is that it's more energy-efficient than previous versions. This means that devices that use WiFi will have longer battery life since they won't have to work as hard to maintain a connection.
-
Increased Capacity
One of the main reasons why WiFi 802.11ax was developed was to increase capacity. The new standard supports up to eight channels, which means it can handle more data traffic than ever. This is perfect for homes and offices with many devices connected to the Internet.
-
Faster Speeds
Of course, WiFi 802.11ax (WiFi 6) also offers faster speeds than its predecessor. The new standard has a theoretical maximum speed of up to nine gigabits per second, nearly three times as fast as WiFi 802.11ac (WiFi 5).
-
Improved Coverage
Finally, WiFi 802.11ax also offers improved coverage. The new standard uses something called OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access), which allows it to send data to multiple devices simultaneously. This means you're less likely to experience dead spots in your home or office.
-
More Efficient Bandwidth Sharing
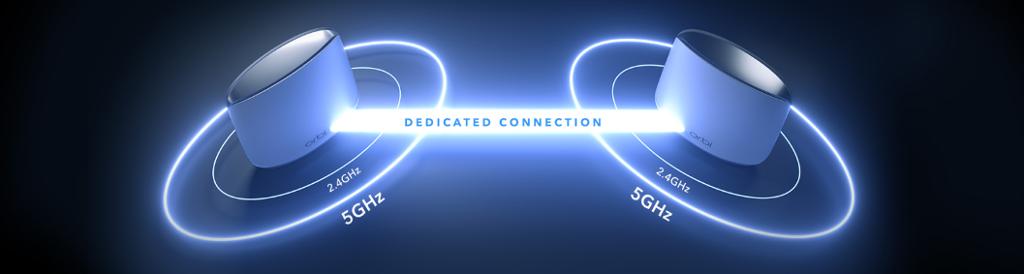
In the past, when multiple devices were trying to connect to the Internet simultaneously, they would have to take turns. This could cause some devices to experience slower speeds than others.
However, with WiFi 802.11ax, each device can have its dedicated connection. This means that all devices can enjoy fast speeds simultaneously without sharing bandwidth.
-
WiFi Sleeping
In homes and offices with many devices connected to the Internet, it's not uncommon for some devices to be inactive for long periods. In the past, these inactive devices would still hog bandwidth and slow down the network for everyone else.
However, with WiFi 802.11ax, inactive devices can enter "sleep" mode. This means that they won't use up any bandwidth until they're needed, which can help improve the network's overall speed.
-
Improved Quality of Service
When you're streaming video or audio, you want to be sure there won't be any hiccups or buffering. With WiFi 802.11ax, you can make sure that your streaming services are at the front of the line thanks to the new standard's improved Quality of Service (QoS) features.
WiFi 5 Vs. WiFi 6: What Is the Difference?
Now that we've answered the question "what is WiFi 802.11ax (WiFi 6)," let's look at how it compares to its predecessor, WiFi 802.11ac (WiFi 5).
The most significant difference between the two standards is speed. As we mentioned before, WiFi 802.11ax has a theoretical maximum speed of up to nine gigabits per second, while WiFi 802.11ac has a theoretical maximum speed of just three gigabits per second.
In terms of range, both standards are fairly similar. However, WiFi 802.11ax does have a slight advantage thanks to its use of OFDMA. This technology allows it to send data to multiple devices simultaneously, which means you're less likely to experience dead spots in your home or office.
Finally, WiFi 802.11ax is more energy-efficient than WiFi 802.11ac, which means that devices that use WiFi will have longer battery life since they won't have to work as hard to maintain a connection.

WiFi 6 Vs. WiFi 6E
As you can imagine, WiFi 6E builds on WiFi 6. The WiFi 6E standard extends the capabilities of the 802.11ax wireless standard into the 6GHz radio frequency band. However, only WiFi 6E devices and applications can operate at 6 GHz frequency.
Compared to the WiFi 6 standard, the WiFi 6E extension creates a 6 GHz 'fast lane' for compatible devices and applications. As a result, it offers lower latency and increased speeds. Unlike WiFi 6 though, older devices can’t take advantage of WiFi 6E’s features because they can’t connect to the 6 GHz band. Most WiFi 6E routers simply connect older devices using the 5 GHz WiFi 6 band instead.
What Device Support WiFi 6?
The answer is probably yes if you're wondering whether your devices support WiFi 802.11ax. Most new smartphones, laptops, and routers support the new standard.
If you're unsure whether your device supports WiFi 802.11ax, the best way to find out is to check with the manufacturer. They should be able to tell you whether or not your device is compatible with the new standard.
How to Get WiFi 6?
If you want to take advantage of the benefits of WiFi 802.11ax, the best way to do it is to upgrade your router.
Most routers released in the past few years support WiFi 802.11ax. However, if your router is more than a few years old, you might need to upgrade to a new one.
While WiFi 6 is efficient, you'll need to purchase reliable hardware to enjoy its full potential. In this regard, there's no better source than NETGEAR. We offer a wide range of WiFi products designed to take advantage of the 802.11ax standard, including the Nighthawk RAX40 and the Orbi AX6000.
If you're looking for the best WiFi experience, check out our WiFi 6 routers and hardware collection.


Meet the Orbi family
Answer a few questions and we'll find the perfect solution for your home



