1. High Constant Load = Higher Operating Temperature
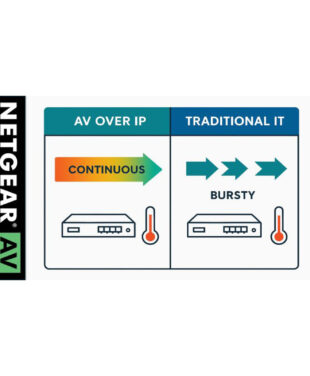
In AV over IP networks, transceivers often run continuously at 90–100% of their capacity. Think of 24/7 video streams, live camera feeds, or multichannel audio. This constant load results in:
- Increased heat generation within the module
- Accelerated aging of laser diodes and circuits
- Higher failure risk if cooling is insufficient
A rule of thumb in electronics: every 10°C temperature increase halves the lifespan of components. At 85°C, the failure rate is up to five times higher than at 40°C [1].
2. Continuous Operation at Maximum Power
In AV environments, downtime is rare. While an IT network might be idle at night, an AV backbone in a hospital or theater runs day and night. This means:
- No time for thermal recovery
- Permanent stress on components
- Faster manifestation of latent manufacturing defects
Modules operating under full load wear out faster than identical modules in less demanding environments.
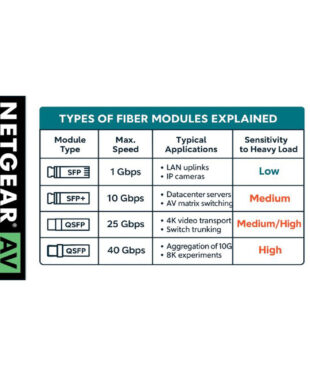
3. Higher Data Rates = Smaller Error Margin
AV over IP networks often push modules to their maximum capacity. For example:
- A 10G SFP+ on 300 meters of multimode fiber for 4K60 video
- A QSFP28 aggregating multiple 4K streams into 100G
In such scenarios, the link budget is tight. Even slight degradation in laser power can immediately lead to:
- Packet loss
- Unstable connections
- Error messages
At higher speeds, tolerances are smaller—what works at 1 Gbps can be catastrophic at 25 or 100 Gbps.
4. Less Than Ideal Environmental Conditions
AV installations are often located in challenging environments:
- Behind LED screens with hot lamps
- In dusty conference halls
- In racks with limited ventilation
Unlike data centers with air conditioning and dust filters, AV locations are often thermally and physically harsher for modules. This increases the risk of:
- Overheating
- Connector contamination
- Mechanical wear
In such situations, industrial-grade modules with higher temperature tolerance are recommended.
Conclusion
AV over IP networks present unique challenges for fiber-optic modules. The combination of high load, continuous operation, maximum data rates, and less-than-ideal environments increases the risk of accelerated wear. This doesn’t mean modules are unsuitable—but they do require more attention and monitoring.
In the next blog, we’ll explore how maintenance and monitoring can extend the lifespan of your modules and prevent failures.
More information
Visit our website to see the AV Solutions.
Discover everything you need to know about AVoIP and building an AV network.
Get free support for your AV project from our senior AV engineers.